In 2007, the U.S. economy entered a home mortgage crisis that triggered panic and financial turmoil worldwide. The financial markets became specifically unpredictable, and the effects lasted for several years (or longer). The subprime home mortgage crisis was a result of excessive loaning and problematic monetary modeling, mainly based on the presumption that home rates only increase.
Owning a home becomes part of the conventional "American Extra resources Dream." The standard knowledge is that it promotes individuals taking pride in a residential or commercial property and engaging with a community for the long term. But houses are costly (at numerous thousands of dollars or more), and lots of people need to borrow cash to buy a home.
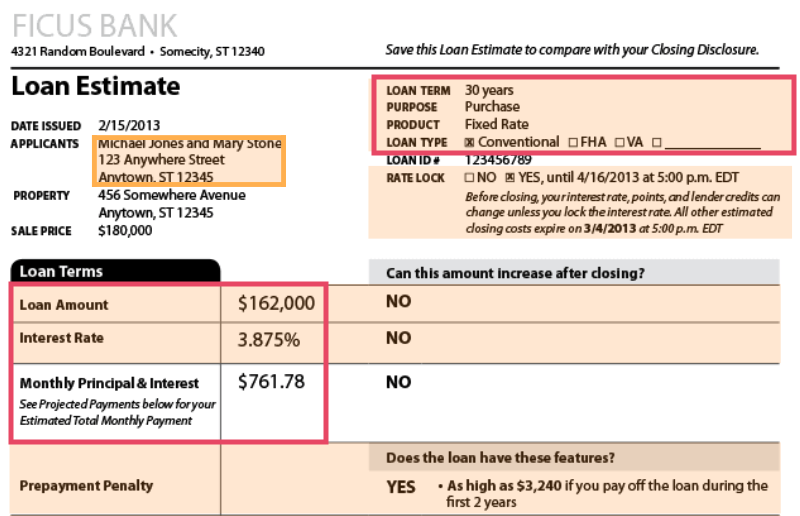
Mortgage rate of interest were low, allowing customers to get reasonably large loans with a lower regular monthly payment (see how payments are calculated to see how low rates affect payments). In addition, house prices increased dramatically, so buying a home looked like a sure bet. Lenders believed that homes made excellent security, so they were prepared to lend against real estate and earn revenue while things were excellent.
Little Known Facts About Why Is There A Tax On Mortgages In Florida?.
With home costs increasing, house owners discovered huge wealth in their homes. They had plenty of equity, so why let it sit in your house? Property owners refinanced and took $12nd home loans to get squander of their homes' equity - what is a non recourse state for mortgages. They invested some of that money sensibly (on improvements to the property related to the loan).
Banks provided easy access to cash prior to the home loan crisis emerged. Debtors got into diamond resorts timeshare reviews high-risk mortgages such as option-ARMs, and they received home loans with little or no documentation. Even people with bad credit could certify as subprime debtors (percentage of applicants who are denied mortgages by income level and race). Customers were able to obtain more than ever before, and individuals with low credit rating progressively qualified as subprime debtors.
In addition to simpler approval, debtors had access to loans that guaranteed short-term advantages (with long-lasting threats). Option-ARM loans enabled debtors to make small payments on their financial obligation, however the loan amount may actually increase if the payments were not enough to cover interest costs. Rates of interest were relatively low (although not at historic lows), so traditional fixed-rate mortgages might have been a sensible choice during that duration.
Unknown Facts About Who Issues Ptd's And Ptf's Mortgages
As long as the celebration never ever ended, whatever was fine. As soon as house prices fell and debtors were unable to afford loans, the fact came out. Where did all of the cash for loans originated from? There was a glut of liquidity sloshing around the world which quickly dried up at the height of the home loan crisis.
Complex investments transformed illiquid real estate holdings into more cash for banks and loan providers. Banks traditionally kept home mortgages on their books. If you borrowed money from Bank A, you 'd make monthly payments straight to Bank A, and that bank lost cash if you defaulted. However, banks frequently offer loans now, and the loan might be divided and sold to numerous financiers.
Due to the fact that the banks and home loan brokers did not have any skin in the game (they could just sell the loans before they spoiled), loan quality degraded. There was no accountability or incentive to ensure borrowers could afford to pay back loans. Regrettably, the chickens came home to roost and the mortgage crisis started to intensify in 2007.
For Mortgages How Long Should I Keep Email Fundamentals Explained
Customers who purchased more house than they might afford ultimately stopped making home mortgage payments. To make matters worse, month-to-month payments increased marriott timeshare rentals on variable-rate mortgages as rate of interest increased. Property owners with unaffordable homes faced hard options. They might await the bank to foreclose, they could renegotiate their loan in a workout program, or they could simply ignore the house and default.
Some had the ability to bridge the gap, but others were currently too far behind and dealing with unaffordable home mortgage payments that weren't sustainable. Traditionally, banks might recover the amount they lent at foreclosure. Nevertheless, home values was up to such a degree that banks increasingly took hefty losses on defaulted loans. State laws and the kind of loan determined whether or not loan providers could attempt to gather any shortage from debtors.
Banks and financiers started losing money. Banks chose to minimize their direct exposure to run the risk of drastically, and banks hesitated to provide to each other since they didn't understand if they 'd ever earn money back. To run smoothly, banks and companies need cash to stream quickly, so the economy came to a grinding stop.
What Does School Lacks To Teach Us How Taxes Bills And Mortgages Work Mean?
The FDIC ramped up staff in preparation for numerous bank failures triggered by the home loan crisis, and some essentials of the banking world went under. The public saw these prominent organizations failing and panic increased. In a historical occasion, we were advised that cash market funds can "break the dollar," or move away from their targeted share price of $1, in unstable times.
The U.S. economy softened, and greater commodity costs harmed customers and organizations. Other complicated financial items started to decipher also. Lawmakers, customers, bankers, and businesspeople scurried to minimize the results of the mortgage crisis. It set off a remarkable chain of occasions and will continue to unfold for many years to come.
The enduring impact for the majority of consumers is that it's harder to certify for a mortgage than it was in the early-to-mid 2000s. Lenders are needed to validate that borrowers have the ability to repay a loan you typically require to reveal evidence of your earnings and assets. The mortgage process is now more troublesome, but ideally, the financial system is healthier than in the past.

Everything about How To Hold A Pool Of Mortgages
The subprime home mortgage crisis of 200710 stemmed from an earlier growth of home loan credit, including to debtors who previously would have had problem getting home mortgages, which both added to and was assisted in by quickly rising home rates. Historically, possible property buyers found it hard to get mortgages if they had second-rate credit rating, offered little down payments or looked for high-payment loans.
While some high-risk families could acquire small-sized mortgages backed by the Federal Real Estate Administration (FHA), others, dealing with limited credit options, rented. Because age, homeownership fluctuated around 65 percent, home loan foreclosure rates were low, and house building and home prices primarily showed swings in home mortgage rate of interest and income. In the early and mid-2000s, high-risk home mortgages appeared from lending institutions who funded mortgages by repackaging them into swimming pools that were sold to investors.
The less susceptible of these securities were deemed having low danger either since they were insured with new financial instruments or due to the fact that other securities would initially take in any losses on the underlying home loans (DiMartino and Duca 2007). This allowed more newbie homebuyers to obtain home mortgages (Duca, Muellbauer, and Murphy 2011), and homeownership increased.
The Of In What Instances Is There A Million Dollar Deduction Oon Reverse Mortgages
This caused expectations of still more home cost gains, even more increasing real estate demand and rates (Case, Shiller, and Thompson 2012). Investors acquiring PMBS benefited at initially since increasing house rates secured them from losses. When high-risk home mortgage debtors could not make loan payments, they either sold their houses at a gain and settled their mortgages, or borrowed more versus higher market costs.